Whether you’ve been using crack and need to pass a drug test or have a loved one who is addicted to the drug, you may wonder how long crack stays in your system. Furthermore, the length of time crack stays in the body is used to determine what medical attention, if any, is required when this individual agrees to get help and goes to detox. There are many types of drug tests, like hair, urine, blood, and saliva, that all detect cocaine metabolites for varying lengths of time. Similarly, crack affects different parts of the body in different ways, so depending on the type of test used, crack stays in your system for varying lengths of time.
Crack, which is derived from cocaine and is one of the most popular illegal drugs, can be detected in urine for up to four days after a person’s last dose, whereas hair tests may detect crack for a year or more. On the other hand, crack cocaine is only detected in saliva for 24 hours after use and in blood for 12 hours after use. However, it’s important to note that these numbers are based on averages – there are a lot of additional factors that influence how long the drug stays in one’s system.
People generally know that crack cocaine is a dangerous and addictive drug, but many people fall victim to the drug each and every year. To better understand the ways in which the body reacts to and processes the drug, let’s take a closer look into what crack is and how it affects the body.
What is Crack?
Crack is a form of cocaine that is smoked or injected to achieve a strong, euphoric, and energetic high. During manufacturing, hydrochloride is removed from cocaine by combining the powder with baking soda, leaving behind a potent substance in the form of hard crystals. When heated, the crystals spark and make a popping sound, which is where the name crack comes from. However, some people may refer to crack as freebase cocaine.
Cocaine is a potent stimulant that produces an intense high characterized by a boost in mental and physical processes. When synthesized into crack, the substance becomes even stronger, producing a more intense high. Being highly concentrated, crack is a highly addictive substance that has an array of negative effects on the mind and body.
When crack enters the body, the effects occur in less than a minute and peak around five minutes. Overall, the high produced only lasts about 30-60 minutes. Even though crack stays in the system for varying lengths of time, the high is short-lived, which often leads people to compulsively seek increasing amounts of the drug.
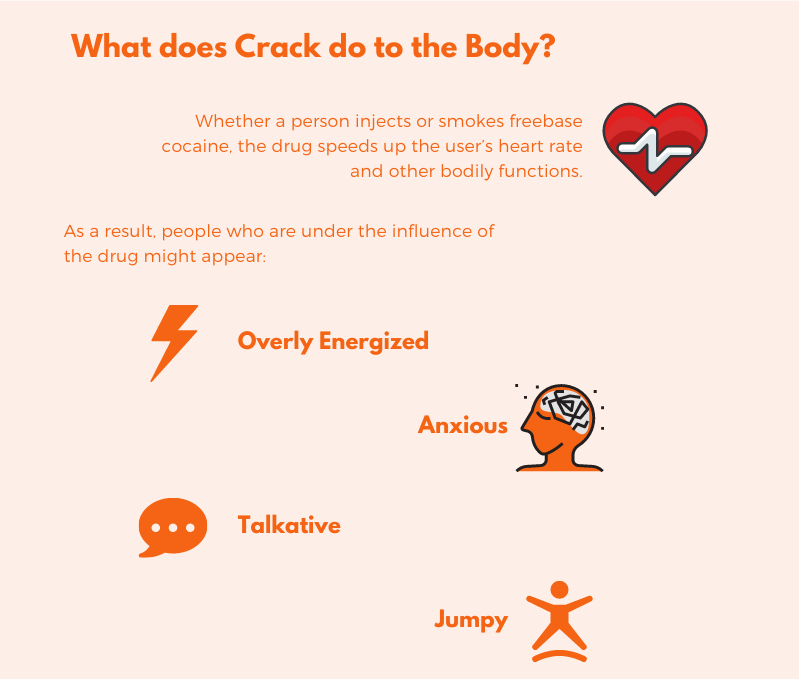
In the short term, it can cause sleep disturbances, paranoia, and even hallucinations or delusions.[1]
Unfortunately, the long term effects of crack cocaine on the body are even more devastating. Long term crack abuse can lead to:[2]
- Impaired cognitive functioning
- Risk of infection due to shared needles, poor hygiene, and risk-taking behaviors
- Damage to the heart, lungs, or other areas of the cardiovascular system
- Increased risk of heart attack
- Mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or psychosis
How Long Does Crack Stay in Your System?
There are many variables that influence how long crack cocaine stays in a person’s system, such as:
- How long you have been using crack cocaine – If you have been using crack on a daily basis for two years, your body will have more of the drug built up in your system over time than someone who has only been smoking crack for one week. The more cocaine metabolites you have in your system, the easier the drug is to detect in a drug test. As a result, crack remains in your system longer the longer you abuse it.
- How much of the drug you use at a time – Similar to how often and how long crack is used, people who use the drug in higher doses will take longer to metabolize the drug and remove it from their system. On the other hand, if someone has only used crack once, it will be cleared from the body rapidly. This is because people who use higher doses have more cocaine metabolites in their system, so the drug can be detected in various drug tests for longer amounts of time.
- Health and function of the liver – the liver is responsible for metabolizing drugs like crack cocaine in the body. If your liver is damaged or doesn’t function well, it will take longer for it to break the substance into smaller compounds that are easier to metabolize. As a result, someone who has healthy liver functioning may be able to pass a urine test after 48 hours, while someone with liver disease will not.
- Your eating and drinking habits – When dehydrated, drugs are metabolized in the body at a slower rate. If you’re looking to remove crack from your system, increasing your fluid intake might help. However, eating habits affect how long crack stays in your system, as well. For example, if you eat around the same time you use the drug, it might slow down the metabolism of the drug, causing it to stay in your body longer.
Types of Drug Tests to Detect Crack Cocaine
Since there are so many factors that determine how quickly crack cocaine and other drugs are metabolized, it’s hard to say exactly how long substances will stay in a person’s system. Furthermore, there are several types of tests that check for drugs that all detect substances after varying lengths of time. Since each type of drug test has a different detection window, you may be able to pass one test, but not pass another.[3]
- Hair tests: hair tests can detect drugs for a very long time after a person’s last use. When it comes to crack, crack is detected in hair follicles for years.
- Blood tests: blood tests are the least likely to detect crack abuse because the substance has a short half-life. As a result, blood tests only detect crack between 2-12 hours.
- Saliva tests: like blood tests, saliva tests are unlikely to detect crack because all traces of the drug usually leave the saliva within 24-48 hours after a person’s last use.
- Urine tests: urine tests are some of the most common drug tests, but crack is only detected in urine for 1-4 days after the last use. In cases of chronic abuse, the drug can be detected in urine for up to two weeks.[4]
Ultimately, there are a lot of factors that go into determining how long crack cocaine remains in various parts of the body. However, if you’re worried about passing a drug test because you’ve done crack or you can’t stop using to stay clean, it’s likely that you need professional drug addiction treatment.
Crack Addiction Treatment
At PAX Memphis, our highly trained therapists and medical staff are equipped with the tools and resources necessary to help you or a loved one overcome crack cocaine addiction. Getting sober is never easy, but asking for help is the hardest part. Don’t wait any longer, contact us today to learn about our addiction treatment programs.
References:
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/drugfacts/cocaine
- https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/cocaine/what-are-long-term-effects-cocaine-use
- https://www.healthline.com/health/how-long-does-cocaine-stay-in-your-system#drug-test-detection
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3128807/
Medically Reviewed: September 25, 2019

All of the information on this page has been reviewed and verified by a certified addiction professional.